 场景题
场景题
# 🔥 解析URL参数
let url = 'https://campus.meituan.com/index?key=value&key2=value2';
function abstractPara(url) {
const obj = {};
url.slice(url.indexOf('?') + 1).split('&').forEach(item => {
const [key, value] = item.split('=');
obj[key] = value;
})
return obj;
}
console.log(abstractPara(url));
//升级版
function regParseParam(url) {
const paramsStr = /.+\?(.+)$/.exec(url)[1];
const paramArr = paramsStr.split('&');
let paramObj = {};
paramArr.forEach(param => {
if (/=/.test(param)) {
let [key, val] = param.split('=');
val = decodeURIComponent(val);
val = /^\d+$/.test(val) ? parseFloat(val) : val;
if (paramObj.hasOwnProperty(key)) {
paramObj[key] = [].concat(paramObj[key], val);
} else {
paramObj[key] = val;
}
} else {
paramObj[key] = true;
}
})
return paramObj;
}
console.log(regParseParam(url));
//reduce实现
function reduceUrl(url) {
let newUrl = '';
let index = url.indexOf('#')
if (index !== -1) {
newUrl = url.slice(0, index)
} else {
newUrl = url;
}
let ans= newUrl.slice(newUrl.indexOf('?') + 1).split('&').reduce((pre, cur, index, arr) => {
const [key, value=''] = cur.split('=');
pre[key] = value||'';
return pre;
}, {});
return JSON.stringify(ans)
}
console.log(reduceUrl(url));
//解析URL Params为对象
function parseParam(url) {
const paramsStr = /.+\?(.+)$/.exec(url)[1];
const paramsArr = paramsStr.split('&');
let paramsObj = {};
paramsArr.forEach(param => {
if (/=/.test(param)) {
let [key, val] = param.split('=');
val = decodeURIComponent(val);
val = /^\d+$/.test(val) ? parseFloat(val) : val;
if (paramsObj.hasOwnProperty(key)) {
paramsObj[key] = [].concat(paramsObj[key], val);
} else {
paramsObj[key] = val;
}
} else {
paramsObj[param] = true;
}
})
return paramsObj;
}
let url1 = 'http://www.domain.com/?user=anonymous&id=123&id=456&city=%E5%8C%97%E4%BA%AC&enabled';
console.log(parseParam(url1))
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
# 🙋 a == 1 && a == 2
考察 非严格相等
==比较时 ,把对象a转为字符串再比较,a.toString()
重构私有方法toString(),使其在不调用对象原型toString()
var a = {
n: 0,
//私有属性方法
toString: function() {
return ++this.n
}
}
//此时的a.toString()调用的不再是Object.prototype.toString(),而是自己私有的属性方法toString();
if(a == 1 && a == 2 && a ==3) {
console.log("OK")
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
重构对象私有方法toString()
var a = [1,2,3];
a.toString = a.shift;
//此时的a.toString()调用的不再是Object.prototype.toString(),而是自己私有的属性方法toString();
if(a == 1 && a == 2 && a ==3) {
console.log("OK")
}
2
3
4
5
6
利用Object.defineProperty()
Object.defineProperty(window,'a',{
get:function() {
//this指向window.a
this.value ? this.value++ : this.value = 1;
return this.value;
}
})
if(a == 1 && a == 2 && a ==3) {
console.log("OK")
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
var a = {
value: 0,
valueOf: function() {
this.value++;
return this.value;
}
};
console.log(a == 1 && a == 2);//true
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
# a===1 && a===2
var value = 0; //window.value
Object.defineProperty(window, 'a', {
get: function() {
return this.value += 1;
}
});
console.log(a===1 && a===2 && a===3) // true
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
# 发布订阅模式
class EventEmitter {
constructor() {
this.cache = {}
}
on(name, fn) {
if (this.cache[name]) {
this.cache[name].push(fn)
} else {
this.cache[name] = [fn]
}
}
off(name, fn) {
let tasks = this.cache[name]
if (tasks) {
const index = tasks.findIndex(f => f === fn || f.callback === fn)
if (index >= 0) {
tasks.splice(index, 1)
}
}
}
emit(name, once = false, ...args) {
if (this.cache[name]) {
// 创建副本,如果回调函数内继续注册相同事件,会造成死循环
let tasks = this.cache[name].slice()
for (let fn of tasks) {
fn(...args)
}
if (once) {
delete this.cache[name]
}
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
# 关闭页面后发请求
navigator.sendBeacon()
用于满足统计和诊断代码的需要,尝试在卸载(unload)前发请求
当用户代理成功把数据加入传输队列,sendBeacon() 返回 true,否则返回 false
# 离开页面可靠发请求
默认,XHR请求异步且非阻塞
有被遗弃的风险,无法保证任何幕后工作都能完成
浏览器设计假设当一个页面被关闭时,没有必要继续处理它排队的任何后台进程
1、延迟用户操作,但是会阻塞主线程,导致性能问题
2、指示浏览器保留未完成的请求,使用fetch的keepalive标志,将相应的请求保持打开状态,即使该请求页面已终止
# 大数相加
function solve(s, t) {
let len = Math.max(s.length, t.length);
const ss = s.padStart(len, "0").split("");
const tt = t.padStart(len, "0").split("");
let flag = 0;
for (let i = len - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
let sum = +ss[i] + +tt[i] + flag;
ss[i] = sum % 10;
flag = sum > 9 ? 1 : 0;
}
if (flag === 1) {
ss.unshift(1);
}
return ss.join("");
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
# input和object双向绑定?
var Person = {}
var name = null
Object.defineProperty(Person, 'name', {
get: function () {
return name
},
set: function (newV) {
name = newV
}
})
let p = document.getElementById('ppp')
let ipt = document.getElementById('ipt')
ipt.addEventListener('input', function (e) {
Person.name = e.target.value
p.innerText = Person.name
})
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
# 🌈 对象拍平
const entry = {
a: {
b: {
c: {
dd: 'abcdd'
}
},
d: [1]
},
e: 'ae',
b: [1, 2, {c: true}],
};
//转换为如下对象
const output = {
'a.b.c.dd': 'abcdd',
'a.d': [1],
e: 'ae'
};
//method 1
//遍历对象,传入对象的key值和value,再对value进行递归遍历
function flatObj(target) {
let res = {};
const process = (key, value) => {
// 先判断数据类型
if (Object(value) !== value) {
if (key) {
res[key] = value;
}
} else if (Array.isArray(value)) {
for (let i = 0; i < value.length; i++) {
process(`${key}[${i}]`, value[i]);
}
if (value.length === 0) {
res[key] = [];
}
} else {
let objArr = Object.keys(value);
objArr.forEach(item => {
process(key ? `${key}.${item}` : `${item}`, value[item]);
});
if (objArr.length === 0 && key) {
res[key] = {};
}
}
}
process('', target);
return res;
}
let ans = flatObj(entry);
// console.log(ans);
//method 2
function objectFlat(obj = ''){
const res = {};
function flat(item , preKey = ''){
Object.entries(item).forEach(([key,value]) => {
let newKey = key;
// console.log(value,typeof value,Array.isArray(value))
if (Array.isArray(item)){
// console.log('是数组')
newKey = preKey ? `${preKey}[${key}]` : key;
}else{
newKey = preKey ? `${preKey}.${key}` : key;
}
if (value && typeof value === 'object'){
flat(value , newKey);
}else{
res[newKey] = value;
}
})
}
flat(obj);
return res;
}
ans=objectFlat(entry);
console.log(ans)
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
function fLatten(data) {
var result = {};
function recurse(cur, prop) {
//如果输入进来的是不是对象,就将其放在数组中,返回
if (Object(cur) !== cur) {
result[prop] = cur;
//如果输入进来的是数组,长度不为0就递归数组,得出结果
} else {
var isEmpty = true;
for (var p in cur) {
isEmpty = false;
recurse(cur[p], prop ? prop + "." + p : p);
}
if (isEmpty && prop)
result[prop] = {};
}
}
recurse(data, "");
return result;
};
let obj = {
a: 1,
b: {
c: 2,
d: {
e: 2
}
}
}
console.log(fLatten(obj))
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
# 括号匹配
function matchBracket(str) {
const length = str.length;
if (length === 0) return true
const stack = []
const leftSymbols = '{[('
const rightSymbols = ' }]) '
const match = {
"}": "{",
")": "(",
"]": "[",
}
for (let i = 0; i < length; i++) {
const s = str[i]
if (leftSymbols.includes(s)) {
//左括号,压栈
stack.push(s)
} else if (rightSymbols.includes(s)) {
//右括号,判断栈顶(是否出栈)
const top = stack[stack.length - 1]
// @ts- ignore
if (match[s] === top) {
stack.pop()
} else {
return false
}
}
}
return stack.length === 0;
}
console.log(matchBracket('(1+2))*3'))
console.log(matchBracket('(1+2)*3'))
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
# 文件扩展名
function getFileExtension(fileName){
return fileName.slice((fileName.lastIndexOf(".")-1)+2);
}
2
3
# 🔥 数组转树
let arrData = [
{
id: 1, val: '学校', parentId: 0, department: ['部门1', '部门2']
}, {
id: 2, val: '班级1', parentId: 1
}, {
id: 3, val: '班级2', parentId: 1
}, {
id: 4, val: '学生1', parentId: 2
}, {
id: 5, val: '学生2', parentId: 2
}, {
id: 6, val: '学生3', parentId: 3
},
];
// 创建parentId的子节点,没有创建根节点的其他信息,只是创建了根节点的子节点数组,所以返回数组
function arrayToTree(data, parentId) {
let result = [];
for (let i = 0; i < data.length; i++) { // 创建子节点列表
if (data[i].parentId === parentId) {
let obj = {};
deepClone(data[i], obj); // 深拷贝,创建子节点
let children = this.arrayToTree(data, data[i].id) || []; // 递归创建子节点的子节点
if (children.length > 0) {
obj.children = children;
}
result.push(obj);
}
}
return result;
}
function deepClone(obj, newObj) {
for (let key in obj) {
if (obj.hasOwnProperty(key)) {
newObj[key] = typeof obj[key] === 'object' ?
deepClone(obj[key], newObj[key]) :
obj[key];
}
}
}
console.log(arrayToTree(arrData, 1));
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
实现
// 转换前:
let source = [{
id: 1,
pid: 0,
name: 'body'
}, {
id: 2,
pid: 1,
name: 'title'
}, {
id: 3,
pid: 2,
name: 'div'
}];
function jsonToTree(data) {
let ans = [];
if (!Array.isArray(data)) {
return ans;
}
//使用map,将当前对象id和当前对象对应存储
let map = {};
data.forEach(item => {
map[item.id] = item;
});
data.forEach(item => {
let par = map[item.pid];
if (par) {
(par.children || (par.children = [])).push(item);
} else {
ans.push(item);
}
});
return ans;
}
console.log(jsonToTree(source))
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
# 🌈 数组对象找id
var result = [];
function find(arr, id) {
if (arr == null) return null;
for (let obj of arr) {
if (obj.id === id) {
result = [...result, collect(obj)];
}
find(obj.children, id);
}
}
function collect(obj) {
let ret = obj;
if (obj.children) {
for (let o of obj.children) {
ret = [...ret, ...collect(o)]
}
}
return ret;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
let tree = [
{
id: '1',
name: '节点1',
children: [
{
id: '1-1',
name: '节点1-1',
children: [
{
id: '1-1-1',
name: '节点1-1-1'
}
]
},
{
id: '1-2',
name: '节点1-2'
}
]
},
{
id: '2',
name: '节点2',
children: [
{
id: '2-1',
name: '节点2-1'
}
]
}
];
function findNode(tree, func) {
let node, curTree = [...tree]
for (let i = 0; i < curTree.length; i++) {
if (func(curTree[i])) {
return curTree[i]
}
if (curTree[i].children) {
curTree.splice(i + 1, 0, ...curTree[i].children)
}
}
}
const data = findNode(tree, (node) => {
return node.name === '节点1-1-1'
})
console.log( data)
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
# 循环打印红黄绿
红灯 3s 亮一次,绿灯 1s 亮一次,黄灯 2s 亮一次;让三个灯不断交替重复亮灯?
function red() {
console.log('red');
}
function green() {
console.log('green');
}
function yellow() {
console.log('yellow');
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
# callback
const task = (timer, light, callback) => {
setTimeout(() => {
if (light === 'red') {
red()
}
else if (light === 'green') {
green()
}
else if (light === 'yellow') {
yellow()
}
callback()
}, timer)
}
task(3000, 'red', () => {
task(2000, 'green', () => {
task(1000, 'yellow', Function.prototype)
})
})
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
问题:只完成了一次 流程,如何交替重复 执行?
使用 递归
const step=()=>{
task(3000,'red',()=>{
task(2000,'green',()=>{
task(1000,'yellow',step);
})
})
}
step();
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
# Promise
const task = (timer, light) =>
new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
if (light === 'red') {
red()
}
else if (light === 'green') {
green()
}
else if (light === 'yellow') {
yellow()
}
resolve()
}, timer)
})
const step = () => {
task(3000, 'red')
.then(() => task(2000, 'green'))
.then(() => task(2100, 'yellow'))
.then(step)
}
step()
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
# async/await
const taskRunner=async()=>{
await task(3000,'red');
await task(2000,'green');
await task(1000,'yellow');
taskRunner();
}
taskRunner();
2
3
4
5
6
7
# 隔一秒打印 1 2 3 4
// 闭包实现
for(var i=0;i<5;i++){
(function (i){
setTimeout(function(){
console.log(i);
},i*1000);
})(i);
}
//使用 let块级作用域
for(let i=0;i<5;i++){
setTimeout(function(){
console.log(i);
},i*1000);
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
# 对象 循环引用
const isCycleObject = (obj,parent) => {
const parentArr = parent || [obj];
for(let i in obj) {
if(typeof obj[i] === 'object') {
let flag = false;
parentArr.forEach((pObj) => {
if(pObj === obj[i]){
flag = true;
}
})
if(flag) return true;
flag = isCycleObject(obj[i],[...parentArr,obj[i]]);
if(flag) return true;
}
}
return false;
}
const a = 1;
const b = {a};
const c = {b};
const o = {d:{a:3},c}
o.c.b.aa = a;
console.log(isCycleObject(o))
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
# 🌰 0.1+0.2 === 0.3?
0.1 + 0.2 = 0.30000000000000004 //15个0
一个数出现无限循环,再大的内存计算机也存不下,所以只能存储一个近似值,再取出就会出现精度丢失
在JS中,主流的数值类型是Number,Number采用的是IEEE754规范中64位双精度浮点数编码
优点是可以归一化处理整数和小数,节省存储空间
对于一个整数,可以很轻易转化成十进制或者二进制。但是对于一个浮点数来说,因为小数点的存在,且小数点的位置不固定。解决思路就是使用科学计数法,这样小数点位置就固定了
10进制科学计数法表达式,底数为10,n为整数
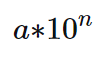
如0.1就可以表示——0.1=1*(10的-1次方)
在IEEE 754标准中类似,计算机只能用二进制(0或1)表示,底数为2,二进制转换为科学记数法的公式如下:
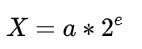
0.1的二进制表示为:
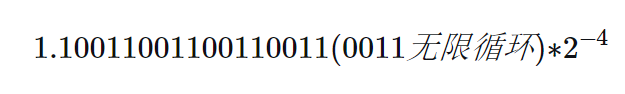
其中,a为0或者1,e为小数点移动的位置
十进制小数转二进制?
十进制小数转二进制,具体做法是:用2乘十进制小数,得到积,将积的整数部分取出,再用2乘余下的小数 部分,又得到一个积,再将积的整数部分取出,如此进行,直到积中的小数部分为零,或者达到所要求的精度为止
把取出的整数部分按顺序排列起来,先取的整数作为二进制小数的高位有效位,后取的整数作为低位有效位。(乘2取整,顺序排列)
举个例子:
27.0转化成二进制为11011.0
先把0.5转换为二进制小数
0.5*2=1.0 //积中小数部分为0
(27) 10=(11011) 2
(0.5) 10=(1.0) 2
合并整数和小数部分可得
(27.5) 10=(11011.1) 2
2
3
4
5
6
7
0.1转为二进制?
0.1 * 2 = 0.2 --------------- 取整数 0,小数 0.2
0.2 * 2 = 0.4 --------------- 取整数 0,小数 0.4
0.4 * 2 = 0.8 --------------- 取整数 0,小数 0.8
0.8 * 2 = 1.6 --------------- 取整数 1,小数 0.6
0.6 * 2 = 1.2 --------------- 取整数 1,小数 0.2
0.2 * 2 = 0.4 --------------- 取整数 0,小数 0.4
0.4 * 2 = 0.8 --------------- 取整数 0,小数 0.8
0.8 * 2 = 1.6 --------------- 取整数 1,小数 0.6
0.6 * 2 = 1.2 --------------- 取整数 1,小数 0.2
...
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
最后 0.1的二进制可以表示为0.000110011……(0011无限循环),因此二进制无法精确保存类似0.1这样的小数
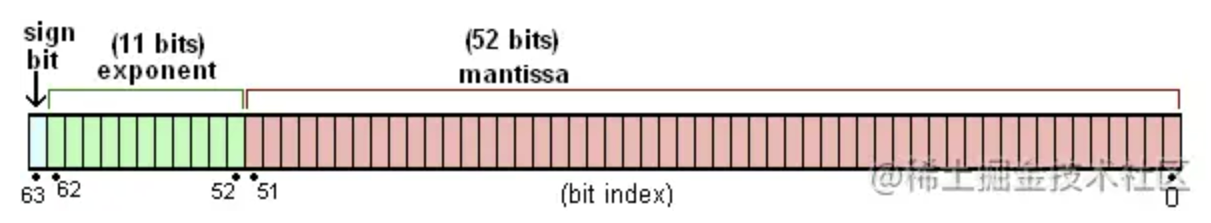
JS存储方式是IEEE 754 标准浮点数表示常用的 双精度浮点数 表示法,其长度为8个字节,即64位比特
64位比特又可分为三个部分:
- 符号位S:第 1 位是正负数符号位(sign),0代表正数,1代表负数
- 指数位E:阶码,中间的 11 位存储指数(exponent),表示次方数,可以为正负数。在双精度浮点数中,指数的固定偏移量为1023
- 尾数位M:最后的 52 位是尾数(mantissa),超出的部分自动进一舍零。(能够真正决定数字精度)
27.0的二进制11011.1转换为科学记数法
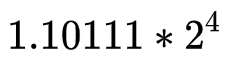
符号位为0(正数),指数位为4+,1023+4,即1027
因为它是十进制的需要转换为二进制,即 10000000011,小数部分为10111,补够52位即: 1011 1000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000
所以27.5存储为计算机的二进制标准形式(符号位+指数位+小数部分 (阶数)),既下面所示
0+100 0000 0011+1011 1000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000
0.1的二进制科学计数法表示
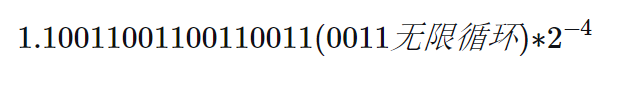
所以0.1存储为计算机的二进制形式为
符号位为0,指数位为 -4 ,1023+(-4)=1019,二进制位 1111 1110 11,E为11位,最终为 011 1111 1011
IEEE754中,循环尾可不能再无限循环,双精度 64 位最多存储的有效整数为 52 位,采用 **就近舍入模式(进1舍0)**存储
0+011 1111 1011+1001 1001 1001 1001 1001 1001 1001 1001 1001 1001 1001 1010
同理,0.2的二进制形式为
0+011 1111 1100+1001 1001 1001 1001 1001 1001 1001 1001 1001 1001 1001 1010
浮点数求和步骤
- 对阶
- 求和
- 规格化
对阶
判断指数位是否相同,即小数位是否对其,若指数位不同,需要对阶保证指数相同
对阶时遵守小阶向大阶看齐原则,*尾数向右移位,每移动一位,指数位加 1 直到指数位相同,即完成对阶。
本示例,0.1 的阶码为 -4 小于 0.2 的阶码 -3,故对 0.1 做移码操作
// 0.1 移动之前
0 + 011 1111 1011+ 1001 1001 1001 1001 1001 1001 1001 1001 1001 1001 1001 1001 1010
// 0.1 右移 1 位之后尾数最高位空出一位,(0 舍 1 入,此处舍去末尾 0)
0 + 011 1111 1100 +1001 1001 1001 1001 1001 1001 1001 1001 1001 1001 1001 1001 101(0)
// 0.1 右移 1 位完成
0 +011 1111 1100 +1100 1100 1100 1100 1100 1100 1100 1100 1100 1100 1100 1100 1101
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
尾数求和
// 0.1 和 0.2 都转化成二进制后再进行运算
0+011 1111 1100+1100 1100 1100 1100 1100 1100 1100 1100 1100 1100 1100 1100 1101 // 0.1
(+) 0+011 1111 1100+1001 1001 1001 1001 1001 1001 1001 1001 1001 1001 1001 1001 1010 // 0.2
= 0+011 1111 1100+10 0110 0110 0110 0110 0110 0110 0110 0110 0110 0110 0110 0110 0111 // 产生进位,待处理
2
3
4
5
规格化和舍入
由于产生进位,阶码需要+1,原阶码为011 1111 1100,+1后得到1000 10,转换为十进制,即1021,此时阶码为1021-1023= -2,此时符号位,指数位分别为0 + 011 1111 1101
尾部进位2位,去除最高位默认的1,因为最低位为1需要进行舍入操作,即在最低有效位上+1,若为0则直接舍去,若为1继续+1
10 0110 0110 0110 0110 0110 0110 0110 0110 0110 0110 0110 0110 0111 // + 1
= 0 0110 0110 0110 0110 0110 0110 0110 0110 0110 0110 0110 0110 1000 // 去除最高位默认的 1
= 0 0110 0110 0110 0110 0110 0110 0110 0110 0110 0110 0110 0110 1000 // 最后一位 0 舍去
= 0011 0011 0011 0011 0011 0011 0011 0011 0011 0011 0011 0011 0100 // 尾数最后结果
2
3
4
因此 IEE 754最终存储如下:
0+011 1111 1101+0011 0011 0011 0011 0011 0011 0011 0011 0011 0011 0011 0011 0100
最高位为1,得到二进制
2^-2 * 1.0011 0011 0011 0011 0011 0011 0011 0011 0011 0011 0011 0011 0100
转换为十进制
0.3 0000 0000 0000 0004
总结
- 精度损失 0.1和0.2转换为二进制出现无限循环情况,JS以64位双精度格式存储数字,最大可存储53位有效数字,超过此长度会被截取掉,造成精度损失
- 对2个64位双精度格式数据计算时,首先进行对阶处理(将阶码对齐,将小数点位置对齐),因此,小阶数在对齐时,有效数字会向右移动,超过有效位数的位被截取掉
- 当两个数据阶码对齐后进行加运算,得到的结果可能超过53位有效数字,超过的位会被截取掉
相加后因浮点数小数位限制截断的二进制数字转换为十进制时变成0.30000000000000004(15个0)
# 💚 组件封装
# 编辑器组件API,滚动加载?
文本编辑器 style value、setValue、getValue、clearContent、config
滚动加载使用的属性
使用offsetTop实现的话
| 属性 | 说明 | 类型 | 默认 | 必传 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| style | ||||
| lazy | 开启懒加载 | boolean or string | false or '.lazy-view' | |
| hasMore | 加载更多 | boolean | true | true |
| isEmpty | 展示空页 | boolean | ||
| isError | 展示错误页 | boolean | ||
| needInit | 初始化&自动调用下拉刷新 | boolean | ||
| distanceToRefresh | 下拉刷新距离 | number | ||
| damping | 最大下拉距离 | number | ||
| autoHeight | 开启自适应高度 | boolean |
自定义页面UI
# Modal组件封装?
- visible控制modal显隐
- title content自定义显示内容
- 点击取消关闭modal,调用onClose回调;点击确认调用confirm回调,关闭modal,点击蒙层mask关闭modal
- animate可关闭/开启动画
# 🌰 代码看输出
考察 函数柯里化
let init = 2
f = init => arg => num => {
console.log('init '+init)
console.log('arg '+arg)
console.log('num '+num)
console.log((init = init + num * arg))
}
f1 = f(5)
calc1 = f1(1)
calc2 = f1(-1)
calc1(1)
calc1(1)
calc2(1)
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
考察node事件循环
process.nextTick(function A() {
process.nextTick(function B() {
console.log(1);
process.nextTick(function D() {
console.log(2)
});
process.nextTick(function E() {
console.log(3)
});
});
process.nextTick(function C() {
console.log(4);
process.nextTick(function F() {
console.log(5)
});
process.nextTick(function G() {
console.log(6)
});
});
});
setTimeout(function timeout() {
console.log('timeout fired')
}, 0)
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
考察class
let a=5
class A{
a=10
fn(){
console.log(this.a)
}
}
const b=new A().fn
b()
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
# 异步任务调度器
JavaScript 实现异步任务调度器 (opens new window)
JS实现一个带并发限制的异步调度器scheduler,保证他同时运行的任务最多2个
class Scheduler {
add(promiseCreator) {}
// ......
}
function timeout(time) {
return new Promise(resolve => {
setTimeout(resolve, time);
});
}
const scheduler = new Scheduler();
const addTask = (time, order) => {
// scheduler.add(() => timeout(time)).then(() => console.log(order));
// then放进里面
scheduler.add(() => timeout(time).then(() => console.log(order)));
};
addTask(1000, '1');
addTask(500, '2');
addTask(300, '3');
addTask(400, '4');
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
不是几个一组,而是完成一个任务就push一个任务进队列
class Scheduler {
constructor(max) {
// 最大可并发任务数
this.max = max;
// 当前并发任务数
this.count = 0;
// 阻塞的任务队列
this.queue = [];
}
async add(fn) {
if (this.count >= this.max) {
// 若当前正在执行的任务,达到最大容量max
// 阻塞在此处,等待前面的任务执行完毕后将resolve弹出并执行
await new Promise(resolve => this.queue.push(resolve));
}
// 当前并发任务数++
this.count++;
// 使用await执行此函数
//执行传进来的函数 等待执行完,这是传的参数
const res = await fn();
// 执行完毕,当前并发任务数--
this.count--;
// 若队列中有值,将其resolve弹出,并执行
// 以便阻塞的任务,可以正常执行
this.queue.length && this.queue.shift()();
// 返回函数执行的结果
return res;
}
}
const sleep = time => new Promise(resolve => setTimeout(resolve, time));
const scheduler = new Scheduler(2);
const addTask = (time, val) => {
scheduler.add(() => {
return sleep(time).then(() => console.log(val));
});
};
addTask(1000, '1');
addTask(500, '2');
addTask(300, '3');
addTask(400, '4');
// 2
// 3
// 1
// 4
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
# 蚂蚁面试题
/*
约定:
title数据类型为string
userId为主键,数据类型为Number
*/
const data = [
{userId: 8, title: 'title1'},
{userId: 11, title: ' other'},
{userId: 15, title: null},
{userId: 19, title: 'title2'}
];
const find = (origin) => {
return {
data: origin,
where: function (obj) {
for (let key in obj) {
if (obj.hasOwnProperty(key)) {
this.data = this.data.filter(v => obj[key].test(v[key]))
}
// return find(this.data) // return在此处写,where只能过滤一个筛选条件
}
return this;
// return find(this.data)
},
orderBy: function (key, order) {
this.data.sort((a, b) => {
if (order == 'desc') {
return b[key] - a[key]
} else {
return a[key] - b[key]
}
})
return this.data
}
}
}
var result = find(data).where({
'title': /\d$/
}).orderBy('userId', 'desc');
console.log(result);
// [{( userId: 19, title: 'title2'}, { userId: 8, title: 'title1' }]
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
# 异步顺序执行
异步调异步
function fn1() {
setTimeout(() => {
console.log('fn1执行')
fn2('fn1传递过去的参数')
}, 1000)
}
function fn2(data) {
setTimeout(() => {
console.log('fn2执行', data)
fn3('fn2传递过去的参数')
}, 1000)
}
function fn3(data) {
setTimeout(() => {
console.log('fn3执行', data)
}, 1000)
}
fn1()
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
Promise
function fn1() {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
console.log('fn1执行')
setTimeout(() => {
console.log('fn1结束')
resolve('fn1传递过去的参数')
}, 1000)
})
}
function fn2(data) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
console.log('fn2执行,接收的参数', data)
setTimeout(() => {
resolve('fn2传递过去的参数')
}, 1000)
})
}
function fn3(data) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
console.log('fn3执行,接收的参数', data)
setTimeout(() => {
resolve('fn3传递过去的参数')
}, 1000)
})
}
fn1().then(fn2).then(fn3).then(res => {
console.log('最后一个', res)
})
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
生成器
返回迭代器的函数,使用yield,函数暂停等待,直到 生成的对象调用下一个next(),调用一次next执行一次yield,暂停
function* main() {
const res1 = yield fn1('开始')
const res2 = yield fn2(res1)
const res3 = yield fn3(res2)
console.log(res3, '全部执行完毕')
}
const task = main()
task.next()
function fn1(data) {
setTimeout(() => {
console.log('fn1执行', data)
task.next('fn1执行完毕')
}, 1000)
}
function fn2(data) {
setTimeout(() => {
console.log('fn2执行', data)
task.next('fn2执行完毕')
}, 1000)
}
function fn3(data) {
setTimeout(() => {
console.log('fn3执行', data)
task.next('fn3执行完毕')
}, 1000)
}
console.log('我是最开始同步执行的')
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
# 串行Promise.all
利用ES6新特性
# Array扩展
// 需要进行功能拓展的方法
const mutationMethods = [
'push',
'pop',
'shift',
]
// 请在此出编写扩展方法
const arrayMethods = Object.create(Array.prototype);
const arrayProto = Array.prototype;
mutationMethods.forEach(method => {
arrayMethods[method] = function (...args) {
const ans = arrayProto[method].apply(this, args);
console.log(`hello ${method}`);
return ans;
}
})
const arr = [1, 2, 3]
arr.__proto__ = arrayMethods;
arr.push(4)
console.log(arr)
arr.pop()
console.log(arr)
arr.shift()
console.log(arr)
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
# CSS
# 🙋 div宽高比例变化
1、非等比放大
vh是视窗单位,也是相对单位。相对视窗的高度。视窗被均分为100单位的vh。能够直接获取高度,而用 % 在没有设置 body 高度的情况下,无法正确获得可视区域的高度
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title></title>
<style type="text/css">
.square {
width: 30%;
height: 30vh;
border: 1px solid red;
background-color: #00FFFF;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="square"></div>
</body>
</html>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
2、指定width为父元素的一个固定百分比,自适应宽度
margin和padding的百分比数值相对父元素宽度计算,将元素垂直方向上的padding值设定为和width相同的百分比绘制出自适应正方形
- 若向容器内添加内容,内容占据一定宽度,设置height为0
- 另一种解决办法:子绝父相,父元素相对定位,text绝对定位(不再占有文档位置,自然不会撑大父元素的height,相对父元素偏移)
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title></title>
<style>
.square2 {
width: 30%;
/*height: 0;*/
padding-bottom: 30%;
border: 1px solid red;
background-color: #00FFFF;
position: relative;
}
.text{
position: absolute;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="square2"></div>
</body>
</html>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
3、设置伪元素的margin-top撑开容器,max-height属性失效,因为其只会对元素的content height起作用
使用子元素撑开content部分的高度,使max-height属性生效
容器和伪元素在垂直方向上存在外边距合并问题,解决方法:父元素设置overflow为hidden,触发BFC布局
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title></title>
<style>
.square3 {
width: 30%;
/* 处理外边距合并 */
overflow: hidden;
border: 1px solid red;
background-color: #00FFFF;
}
.square3::after {
content: '占位符';
display: block;
margin-top: 100%;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="square3"></div>
</body>
</html>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
4、设置垂直方向上的padding撑开父元素,不触发BFC
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title></title>
<style>
.square4 {
width: 30%;
border: 1px solid red;
background-color: #00FFFF;
}
.square4::after {
content: '占位符';
display: block;
padding-top: 100%;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="square4"></div>
</body>
</html>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
CSS伪元素 ::after 创建一个伪元素,作为已选中元素的最后一个子元素。通常配合 content属性为该元素添加内容。这个虚拟元素默认是行内元素
content属性用于在before或after伪元素中插入内容
# 0.5px的线
- 直接设置(兼容性问题)
transform: scaleY(0.5);linear-gradient、box-shadow(各自有兼容性问题)- svg的描边等属性的1px是物理像素的1px
- 使用垂直渐变,上部分透明,下部分配置想要的颜色
background-image: linear-gradient(0deg, #f00 50%, transparent 50%);
# 🙋 12px以下文字
Chrome中做了限制
- font-size最小值为12px,低于12px的 一律按照12px显示
- Chrome认为低于12px的中文对人类不友好
zoom
"变焦",可以改变页面上元素的尺寸,属于真实尺寸。有兼容问题,非标准属性,缩放会改变元素占据空间大小,触发重排
- zoom:50%,表示缩小到原来的一半
- zoom:0.5,表示缩小到原来的一半
.test1 {
font-size: 10px;
zoom: 0.8;
}
.test2 {
font-size: 16px;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
-webkit-transform:scale()
针对Chrome使用webkit前缀
使用scale只对可以**定义宽高的元素生效**。不改变页面布局
.test1 {
font-size: 5px;
display: inline-block;
transform: scale(0.8);
}
.test2 {
font-size: 16px;
//行内元素没有宽高,所以设置display
display: inline-block;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
-webkit-text-size-adjust:none
设定文字大小是否根据设备(浏览器)来自动调整显示大小
- percentage:字体显示的大小;
- auto:默认,字体大小会根据设备/浏览器来自动调整;
- none:字体大小不会自动调整
被废掉了
# 1px效果
- 伪元素+缩放
- 动态viewport+rem(flex)
- vw单位适配(未来推荐)
伪元素+缩放
设计稿中的1px,代码要实现0.5px
缩放 避免 直接写小数像素带来的不同手机的兼容性处理不同
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<style>
/*伪元素实现0.5px border*/
.border::after {
content: "";
/*为了与原元素等大*/
box-sizing: border-box;
position: absolute;
left: 0;
top: 0;
width: 200%;
height: 200%;
border: 1px solid red;
transform: scale(0.5);
transform-origin: 0 0;
}
/*实现0.5px 细线*/
.line::after {
content: '';
position: absolute;
top: 0;
left: 0;
width: 200%;
height: 1px;
background: red;
transform: scale(0.5);
/*更改元素变形的原点*/
transform-origin: 0 0;
}
/*dpr适配 ,当前显示设备的物理像素分辨率与CSS 像素分辨率之比为2*/
@media (-webkit-min-device-pixel-ratio: 2) {
.line::after {
height: 1px;
transform: scale(0.5);
transform-origin: 0 0;
}
}
@media (-webkit-min-device-pixel-ratio: 3) {
.line::after {
height: 1px;
transform: scale(0.333);
transform-origin: 0 0;
}
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="border">
<div class="line"></div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
动态viewport+rem
不仅可解决移动端适配,也解决1px的问题
三种viewport中我们常用的layout viewport(浏览器默认),宽度大于浏览器可视区域宽度,因此会出现横向滚动条
const clientWidth = document.documentElement.clientWidth || document.body.clientWidth
设置meta标签属性避免横向滚动条
<meta
name="viewport"
content="
width=device-width, // viewport宽等于屏幕宽
initial-scale=1.0, // 初始缩放为1
maximum-scale=1.0,
user-scalable=no, // 不允许手动缩放
viewport-fit=cover // 缩放以填充满屏幕
"
>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
flexible的原理——已弃用!
- 根据dpr动态修改initial-scale
- 动态修改viewport大小,以此 统一使用rem布局,viewport动态影响font-size,实现适配
总结
移动端适配主要分为两方面
- 适配不同机型的屏幕尺寸
- 对细节像素的处理。如果直接写
1px,由于 dpr 的存导致渲染偏粗。使用rem 布局计算出对应小数值,有兼容性问题。老项目整体修改viewport成本过高,采用第一种实现方案处理;新项目可动态设置viewport,一键解决适配问题
移动端对 1px 的渲染适配实现起来配置简单、代码简短,能够快速上手
# 🚩 三角形?
通过上下左右 边框 控制三角形的方向,用边框的宽度控制三角形的角度
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<style>
.div {
width: 0px;
height: 0px;
border: 100px solid transparent;
border-bottom-color: blue;
}
</style>
<body>
<div class="div"></div>
</body>
</html>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
# 画圆形
设置值超过50%会怎样?
.circle {
width: 300px;
height: 300px;
background-color: green;
border-radius: 50%;
}
2
3
4
5
6
超过50%,还是圆形
# 画同心圆(类似麻将的五饼)
# CSS实现 偶数 子元素高亮, 排除第二个偶数
# others
# 不整页刷新、前进、后退
使用 pushState + ajax 实现浏览器无刷新前进后退,当一次 ajax 调用成功后将一条 state 记录加入到 history对象中。一条 state 记录包含了 url、title 和 content 属性,在 popstate 事件中可以获取到这个state 对象,使用 content 来传递数据。最后 window.onpopstate 监听响应浏览器的前进后退操作
使用 pushState 来实现有两个问题,一个是打开首页时没有记录,使用 replaceState 将首页的记录替换,另一个是当一个页面刷新时,仍然会向服务器端请求,如果请求的 url 需要后端的配合将其重定向到一个页面
# 数组乱序输出
取出数组第一个元素,随机产生一个索引,将其交换,后面依次类推
Math.round()四舍五入
let ary=[1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9];
for(let i=0;i<ary.length;i++){
let randomIndex=Math.round(Math.random()*(ary.length-1-i))+i;
[ary[i],ary[randomIndex]]=[ary[randomIndex],ary[i]];
}
console.log(ary);
2
3
4
5
6
# 圆形环状进度条
一个正方形div中分两个等宽div,设置overflow:hidden
两个div中分别画两个半圆: border-top、border- left,再旋转-45deg
通过旋转动画指定他们漏出来的角度
# 蚂蚁面试
实现100个url(存放在数组),并发请求,调度器 ,并发数不超过5个,按顺序返回请求结果,class类——批量请求函数,限制并发量
在对象数组中查找对应路由(根据关键词),搜索结果可能不唯一,层次遍历 深度优先搜索 递归查询 拍平查询
/*
约定:
title数据类型为string
userId为主键,数据类型为Number
*/
const data = [
{userId: 8, title: 'title1'},
{userId: 11, title: ' other'},
{userId: 15, title: null},
{userId: 19, title: 'title2'}
];
const find = (origin) => {
return {
data: origin,
where: function (obj) {
for (let key in obj) {
if (obj.hasOwnProperty(key)) {
this.data = this.data.filter(v => obj[key].test(v[key]))
}
// return find(this.data) // return在此处写,where只能过滤一个筛选条件
}
return this;
// return find(this.data)
},
orderBy: function (key, order) {
this.data.sort((a, b) => {
if (order == 'desc') {
return b[key] - a[key]
} else {
return a[key] - b[key]
}
})
return this.data
}
}
}
//查找 data 中,符合条件的数据,并进行排序
var result = find(data).where({
'title': /\d$/
}).orderBy('userId', 'desc');
console.log(result);
// [{( userId: 19, title: 'title2'}, { userId: 8, title: 'title1' }]
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
前端实现动画匀速直线运动,兼容性问题 css,JS如何实现?触动?
